World Health Organization's Perspective on the Prevalence of Stroke Cases in Africa
Causes and preventive measures

Introduction:
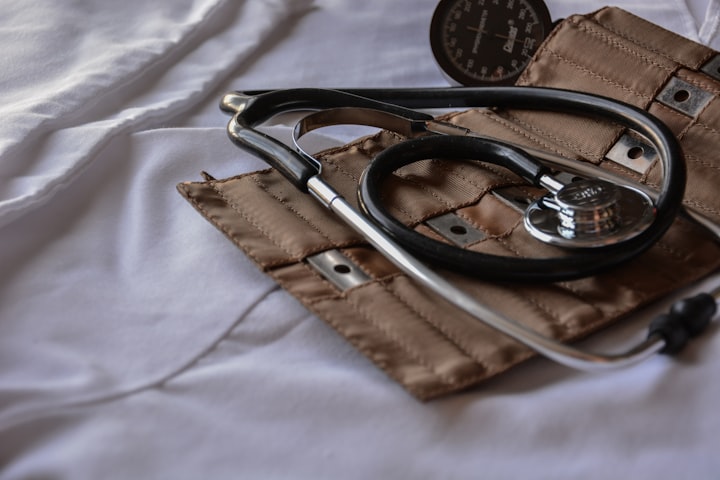
Stroke is a significant public health concern globally, and its impact on populations is particularly noteworthy in Africa. The World Health Organization (WHO) has recognized the rising incidence and prevalence of stroke cases in Africa, highlighting the urgent need for effective prevention strategies and improved access to quality healthcare. This report aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the WHO's opinions on the rampant stroke cases in Africa, including the contributing factors, challenges, and recommended interventions.
Burden of Stroke in Africa:
Africa faces a substantial burden of stroke, with rising incidence rates and significant mortality and disability rates associated with the condition. The WHO estimates that approximately 3.9 million stroke cases occur in Africa each year, making it one of the leading causes of death and disability on the continent. The prevalence of risk factors for stroke, including hypertension, diabetes, obesity, tobacco use, and unhealthy lifestyles, is alarmingly high in many African countries.
Contributing Factors:
Several factors contribute to the rampant stroke cases in Africa. These include:
High prevalence of risk factors: Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is the most significant risk factor for stroke. It is estimated that nearly 30% of adults in Africa have hypertension, making it one of the highest prevalence rates worldwide. Other contributing factors such as diabetes, tobacco use, obesity, and sedentary lifestyles also play a significant role.
Limited healthcare resources: Access to quality healthcare services, including stroke prevention, diagnosis, and treatment, remains a challenge in many African countries. Inadequate infrastructure, shortage of healthcare professionals, limited availability of diagnostic tools, and lack of awareness contribute to delayed or suboptimal stroke care.
Socioeconomic factors: Poverty, limited education, and socioeconomic disparities contribute to the burden of stroke in Africa. These factors impact individuals' ability to access healthcare services, adhere to preventive measures, and manage stroke risk factors effectively.
WHO's Perspective and Interventions:
The World Health Organization has recognized the urgent need to address the rising prevalence of stroke in Africa. Their perspective includes the following key areas:
Stroke prevention: The WHO emphasizes the importance of primary prevention strategies to reduce the incidence of stroke. This includes promoting healthy lifestyles, raising awareness about risk factors, encouraging regular physical activity, promoting a balanced diet, and advocating for tobacco control measures.
Strengthening healthcare systems: The WHO advocates for improving healthcare infrastructure and resources in Africa to enhance stroke care. This involves training healthcare professionals, increasing access to diagnostic tools, and establishing stroke units or specialized centers to provide comprehensive stroke care.
Capacity building: The WHO supports capacity building initiatives to improve stroke care in Africa. This includes training healthcare professionals in stroke management, implementing standardized treatment protocols, and conducting research to understand the unique challenges and risk factors specific to the region.
Advocacy and partnerships: The WHO collaborates with governments, non-governmental organizations, and other stakeholders to advocate for policies and strategies that address the burden of stroke in Africa. These partnerships aim to mobilize resources, raise awareness, and develop sustainable interventions to reduce stroke incidence and improve patient outcomes.
Conclusion:
The prevalence of stroke cases in Africa is a significant public health concern. The World Health Organization recognizes the urgent need to address this issue and has outlined key perspectives and interventions to mitigate the burden of stroke in Africa. By focusing on prevention strategies, strengthening healthcare systems, capacity building, and fostering partnerships, it is possible to reduce the incidence of stroke, improve patient outcomes, and enhance the overall well-being of individuals affected by this condition in Africa. Efforts from multiple stakeholders, including governments, healthcare professionals, and communities, are crucial in effectively combating the rampant stroke cases and ensuring a healthier future for the African population.
Precautions to Mitigate the Burden of Stroke in Africa
Introduction:
Given the alarming prevalence of stroke cases in Africa, it is imperative to prioritize preventive measures that can help mitigate the burden of this condition. By adopting appropriate precautions, individuals can reduce their risk factors for stroke and promote overall cardiovascular health. This report focuses on suggested precautions recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO) to combat the rising incidence of stroke in Africa.
Awareness and Education:
Raising awareness about stroke risk factors, warning signs, and preventive measures is crucial in empowering individuals to take proactive steps. The WHO advocates for public health campaigns that educate communities about the importance of recognizing the signs of stroke, such as sudden weakness or numbness, difficulty speaking or understanding, severe headaches, and vision problems. Promoting knowledge about the risk factors, including hypertension, diabetes, smoking, obesity, and sedentary lifestyles, can encourage individuals to make informed lifestyle choices and seek appropriate medical care.
Blood Pressure Management:
Hypertension is a major risk factor for stroke, and its prevalence is particularly high in Africa. Regular monitoring of blood pressure is vital, and individuals with hypertension should work closely with healthcare professionals to manage their condition effectively. The WHO recommends lifestyle modifications, including reducing salt intake, adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, limiting alcohol consumption, and avoiding tobacco use.
Diabetes Control:
Diabetes is another significant risk factor for stroke. Managing diabetes through medication, regular blood sugar monitoring, and adopting a healthy lifestyle is crucial. The WHO emphasizes the importance of promoting diabetes awareness, early diagnosis, and access to affordable and quality diabetes care in Africa.
Tobacco Control:
Tobacco use is a leading preventable cause of stroke. The WHO supports tobacco control measures, including increasing taxes on tobacco products, implementing comprehensive smoke-free policies, enforcing bans on tobacco advertising, and providing support for smoking cessation programs. By promoting a tobacco-free environment, the burden of stroke can be significantly reduced.
Healthy Diet:
A balanced diet plays a crucial role in preventing stroke. The WHO recommends a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, while limiting the intake of saturated and trans fats, salt, and added sugars. Encouraging the consumption of locally available nutritious foods, promoting traditional diets, and educating communities about healthy food choices can have a significant impact on stroke prevention.
Physical Activity:
Regular physical activity is essential for maintaining cardiovascular health and reducing the risk of stroke. The WHO recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week, along with muscle-strengthening activities. Encouraging community-based physical activities, promoting active transportation, and incorporating exercise into daily routines are effective strategies to promote physical activity in Africa.
Access to Quality Healthcare:
Improving access to quality healthcare services is crucial for stroke prevention and management. The WHO advocates for strengthening healthcare systems in Africa by increasing the number of healthcare professionals, improving infrastructure, and ensuring the availability of essential diagnostic tools and medications. Enhancing primary healthcare services, establishing stroke units or specialized centers, and training healthcare professionals in stroke management can significantly improve patient outcomes.
Community Engagement and Support:
Engaging communities in stroke prevention efforts can foster sustainable change. The WHO encourages community-based interventions, such as support groups, educational programs, and outreach campaigns. By involving community leaders, local organizations, and individuals, awareness can be raised, and preventive measures can be effectively implemented and sustained.
Conclusion:
Preventing stroke requires a multi-faceted approach that involves individuals, communities, healthcare professionals, and policymakers. By implementing the suggested precautions recommended by the World Health Organization, the burden of stroke in Africa can be mitigated. Raising awareness, managing risk factors, adopting healthy lifestyles, and ensuring access to quality healthcare services are key steps in preventing stroke and promoting overall cardiovascular health. Collaboration and sustained efforts from various stakeholders are essential to achieve meaningful and lasting impact in reducing stroke cases and improving the well-being of individuals in Africa.
About the Creator
Abel Omikunle
Abel Omikunle is a young man of 48 and a highly experienced professional in the field of sales and marketing management .
An exceptional goal getter and a veteran leader that has been able to create and build copious leaders in diverse field




Comments
There are no comments for this story
Be the first to respond and start the conversation.