Top 5 New Things you must Know about-Debunking common myths about plant-based diets
Separating Fact from Fiction: Clearing Up Misconceptions About Plant-Based Eating
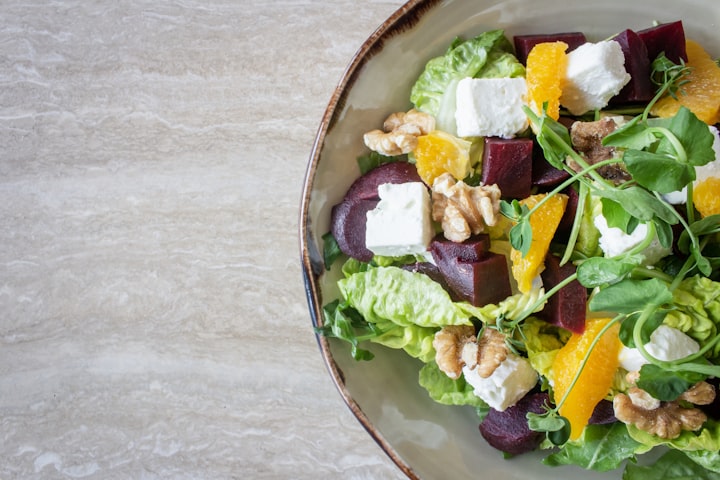

1)Plant-based diets are not nutritionally adequate:
Plant-based diets, which are based on foods primarily derived from plants, have been gaining popularity in recent years due to their many health benefits. However, there is a common myth that plant-based diets are not nutritionally adequate. In this article, we will dispel this myth and explore the truth about the nutritional adequacy of plant-based diets.
First and foremost, it is important to understand that plant-based diets can provide all the essential nutrients required for optimal health. This includes protein, iron, calcium, and vitamins B12 and D. While it is true that some plant-based sources of these nutrients are not as well absorbed as animal-based sources, a properly planned plant-based diet can easily meet all of our nutritional needs.
For example, plant-based sources of protein, such as beans, lentils, nuts, and tofu, are highly nutritious and contain all the essential amino acids needed for optimal health. Iron from plant-based sources, such as fortified cereals and leafy greens, can be just as bioavailable as iron from animal sources when consumed with vitamin C-rich foods. Calcium-rich plant-based foods, such as kale and fortified plant milks, can also provide adequate amounts of this mineral.
Vitamin B12 is an important nutrient that is only found in animal-based foods, so it can be a concern for those following a strictly plant-based diet. However, vitamin B12 is available in fortified plant-based foods, such as plant milks and breakfast cereals, and can also be obtained through supplementation.
Vitamin D, which is important for bone health, is also commonly obtained from animal-based foods. However, it can also be obtained through sunlight exposure and fortified plant-based foods. Additionally, vitamin D supplementation can be used to ensure adequate intake for those following a plant-based diet.
In conclusion, plant-based diets can be nutritionally adequate and provide all the essential nutrients needed for optimal health. The key to a healthy plant-based diet is to choose a variety of nutrient-dense foods, such as whole grains, legumes, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds, and to consider vitamin B12 and vitamin D supplementation as needed. With proper planning, plant-based diets can provide all the nutrients required for optimal health and well-being.
2)Plant-based diets are expensive and limit food choices:
Plant-based diets have gained popularity in recent years as a healthful and environmentally sustainable way of eating. However, one common misconception is that plant-based diets are expensive and limit food choices. In this article, we will dispel this myth and show how plant-based diets can be both affordable and offer a diverse range of food options.
First, it is important to note that plant-based diets can be as inexpensive or expensive as you make them. While some specialty plant-based products, such as vegan meat substitutes, can be more expensive than their animal-based counterparts, the staples of a plant-based diet, such as fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains, are often very affordable. In fact, studies have shown that a plant-based diet can be less expensive than a diet that includes animal products.
Furthermore, plant-based diets offer a wide range of food options, including fresh and frozen fruits and vegetables, legumes, whole grains, plant-based milks, and meat substitutes. With the growing popularity of plant-based eating, grocery stores now offer a wider selection of plant-based products, making it easier and more convenient to follow a plant-based diet.
In addition, plant-based diets can be culturally diverse, with traditional cuisines from around the world offering a variety of flavorful and nutrient-dense plant-based dishes. For example, Indian cuisine features many flavorful vegetarian dishes, while Ethiopian cuisine includes a variety of flavorful stews and injera made from lentils and other legumes.
It is also worth mentioning that plant-based diets can be very flexible, allowing for a variety of food choices and meal options. Whether you prefer raw, cooked, or a combination of both, plant-based diets offer the opportunity to experiment with new ingredients and flavors.
In conclusion, the idea that plant-based diets are expensive and limit food choices is simply a myth. With the growing popularity of plant-based eating, the availability and affordability of plant-based products have greatly improved, offering a wide range of food options that are both delicious and nutritious. Whether you are interested in a healthful, environmentally sustainable, or culturally diverse diet, a plant-based diet is a great choice.
3)Plant-based diets do not provide enough protein:
Plant-based diets have become increasingly popular in recent years, but one of the most common misconceptions about this way of eating is that it does not provide enough protein. This simply isn't true. In fact, a well-planned plant-based diet can easily provide all the protein a person needs to maintain good health.
One of the reasons this myth persists is that many people associate protein with animal products, such as meat, dairy, and eggs. However, protein is a macronutrient that can be found in many plant-based foods as well. Beans, lentils, nuts, seeds, and whole grains are all excellent sources of plant-based protein.
It's also worth noting that the human body does not need large amounts of protein. The recommended daily allowance for protein is 0.8 grams per kilogram of body weight. This means that an average adult needs about 46 grams of protein per day. A well-balanced plant-based diet can easily meet this requirement.
For those who are skeptical, it's worth mentioning that there are many elite athletes and bodybuilders who follow plant-based diets and have no trouble building and maintaining muscle mass. Plant-based protein sources, such as soy, quinoa, and peas, contain all of the essential amino acids the body needs to build and repair muscle.
It's important to keep in mind that not all plant-based diets are created equal. A diet that primarily consists of junk food and processed carbohydrates will not provide adequate amounts of protein, or any other essential nutrient. However, a well-planned plant-based diet that includes a variety of whole foods, such as whole grains, legumes, vegetables, and nuts, can provide all the nutrients a person needs to thrive.
In conclusion, the myth that plant-based diets do not provide enough protein is simply not true. A well-planned plant-based diet can provide all the protein a person needs to maintain good health, and even support athletic performance. By including a variety of plant-based protein sources in your diet, you can easily meet your daily protein needs.
4)Plant-based diets do not support athletic performance:
Plant-based diets have been the subject of many myths and misconceptions in recent years, and one of the most common is that they do not support athletic performance. This simply is not true. In fact, numerous studies and athletes have shown that a well-planned plant-based diet can provide all the necessary nutrients for optimal athletic performance.
One of the biggest misconceptions about plant-based diets is that they do not provide enough protein. Protein is an essential nutrient for building and repairing muscle, and it is often assumed that athletes need to consume large amounts of animal-based protein to meet their needs. However, there are many plant-based sources of protein that can provide all the protein an athlete needs, including legumes, nuts, and seeds.
Another myth about plant-based diets is that they do not provide enough iron. Iron is essential for transporting oxygen to the muscles, and it is often assumed that only animal-based iron is easily absorbed by the body. However, plant-based sources of iron, such as leafy greens, beans, and fortified cereals, can provide all the iron an athlete needs. In addition, vitamin C, which is abundant in fruits and vegetables, can enhance iron absorption from plant-based sources.
Plant-based diets also provide other important nutrients for athletic performance, including carbohydrates, which are the primary energy source for muscles during exercise, and healthy fats, which help to reduce inflammation and support joint health.
Finally, there is evidence that plant-based diets can actually improve athletic performance by reducing inflammation and oxidative stress. This can help to reduce muscle damage and improve recovery times, allowing athletes to train harder and perform better.
In conclusion, a well-planned plant-based diet can provide all the nutrients an athlete needs for optimal performance, and there is evidence that it can even improve performance by reducing inflammation and oxidative stress. So, for athletes who are looking for a healthy, sustainable way to fuel their performance, a plant-based diet is definitely worth considering.
5)Plant-based diets are not sustainable for feeding the world's population:
Plant-based diets have gained a lot of popularity in recent years, but one of the most persistent criticisms is that they are not sustainable for feeding the world's population. This myth has its roots in the idea that plant-based diets are not efficient enough to produce enough food to feed everyone, and that they require too much land, water, and other resources. However, the reality is more complex and nuanced.
First, it's important to understand that the efficiency of food production depends on many factors, including the type of crops being grown, the use of fertilizers, and the efficiency of the farming method. For example, industrial agriculture systems that rely heavily on monoculture crops and chemical inputs are often less efficient than agroecological farming systems that focus on diverse crop rotations and the use of natural inputs.
Additionally, the amount of land and resources needed for food production can be greatly reduced by using more efficient farming methods and by reducing food waste. For example, studies have shown that reducing food waste could free up as much as 25% of the land currently used for agriculture. Moreover, plant-based diets have been shown to have a lower environmental impact than diets that are heavy in animal products, as the production of animal-based foods is more resource-intensive and results in higher greenhouse gas emissions.
Another important factor to consider is that not all plant-based diets are equal. A diet based on highly processed foods and simple sugars is less nutritious and sustainable than a diet that focuses on whole, minimally processed foods, such as whole grains, legumes, and vegetables. Furthermore, diets that include significant amounts of plant-based meat substitutes can also have a significant environmental impact, as the production of these products often relies on large inputs of energy and other resources.
In conclusion, plant-based diets can be sustainable for feeding the world's population, but only if they are based on whole, minimally processed foods, and if they are produced in a way that is environmentally sustainable. By reducing food waste and embracing more efficient and sustainable farming methods, we can create a food system that is both nutritious and sustainable for everyone.




Comments
There are no comments for this story
Be the first to respond and start the conversation.