Plastic : Harmful Effects
Harmful Effects of Using Plastic
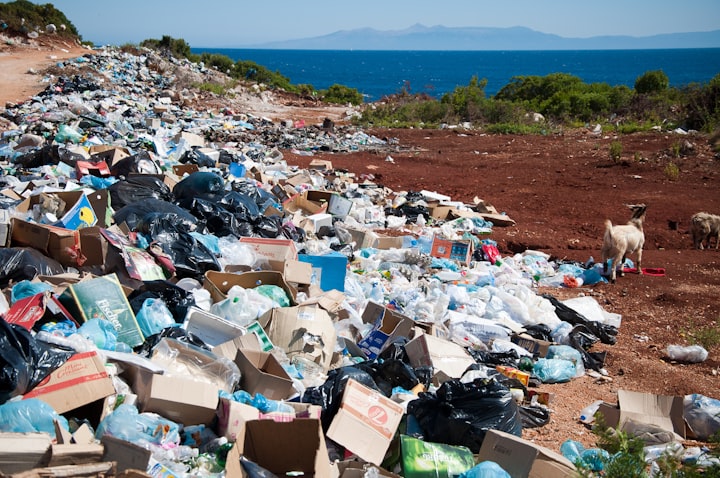

Plastic has become an integral part of our lives. We use it every day, from the packaging of the products we buy to the containers we store our food in. Plastic is cheap, convenient, and durable. However, the overuse of plastic has led to severe environmental and health problems. This article will discuss the harmful effects of plastic and how we can reduce our plastic consumption.
Environmental Pollution
Plastic pollution is a severe environmental problem that has gained increasing attention in recent years. Plastic is not biodegradable and can persist in the environment for hundreds of years. Plastic debris pollutes our oceans, rivers, and lakes and harms marine life. According to a study by the Ellen MacArthur Foundation, there will be more plastic than fish in the oceans by 2050 if we do not take immediate action.
Health Risks
Plastic contains harmful chemicals that can leach into our food and water. One of the most well-known chemicals found in plastic is Bisphenol A (BPA). BPA is used in the production of polycarbonate plastics and epoxy resins. It has been linked to cancer, obesity, and reproductive problems. Another harmful chemical found in plastic is phthalates. Phthalates are used to make plastic soft and flexible. They have been linked to asthma, diabetes, and fertility problems.
Cancer: One of the most dangerous effects of plastic on human health is its potential to cause cancer. Many types of plastics contain harmful chemicals, such as bisphenol A (BPA), phthalates, and styrene, that are known to cause cancer. When these chemicals come into contact with food or beverages, they can leach into them, posing a significant risk to human health.
Hormone disruption: Plastic also contains chemicals that can disrupt the body's hormone balance. BPA, for instance, mimics estrogen and can interfere with the body's endocrine system, which regulates hormones. This can lead to a range of health problems, including infertility, obesity, and diabetes.
Respiratory problems: Burning plastic releases toxic fumes that can cause respiratory problems. Inhaling these fumes can cause coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath, and can even lead to more severe respiratory illnesses like asthma.
Skin irritation: Many plastics contain additives that can cause skin irritation, especially in people with sensitive skin. The irritation can be mild to severe, depending on the type of plastic and the individual's sensitivity to it.
Allergies: Plastic can also cause allergic reactions in some people. The symptoms of a plastic allergy can include itching, hives, and swelling.
Birth defects: Exposure to certain types of plastic can increase the risk of birth defects in newborns. For instance, phthalates, which are often found in plastic products, have been linked to an increased risk of birth defects in male infants.
Obesity: There is also evidence that plastic exposure may contribute to obesity. BPA, in particular, has been shown to disrupt the endocrine system, which can lead to weight gain and obesity.
Landfills
Plastic waste takes up a lot of space in landfills. Landfills are designed to keep waste from the environment, but plastic waste can take hundreds of years to decompose. When plastic does eventually break down, it releases harmful chemicals into the soil and groundwater. These chemicals can contaminate our drinking water and harm our health.
Microplastics
Microplastics are tiny plastic particles that are less than 5mm in size. They are created when larger plastic debris breaks down into smaller pieces. Microplastics are found in our oceans, rivers, and lakes, and they have also been found in our food and drinking water. Microplastics can harm marine life, and they have also been linked to health problems in humans.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Plastic production contributes to greenhouse gas emissions. The production of plastic requires fossil fuels, which contribute to climate change. The transportation and disposal of plastic waste also contribute to greenhouse gas emissions.
How to Reduce Plastic Consumption
Use Reusable Bags
Bring your reusable bags when shopping instead of using plastic bags.
Use Reusable Containers
Use reusable containers to store food instead of using plastic containers.
Say No to Plastic Straws
Say no to plastic straws and use alternatives like metal or paper straws.
Choose Glass or Stainless Steel Bottles
Choose glass or stainless steel bottles instead of plastic bottles.
Avoid Single-Use Plastics
Avoid single-use plastics like disposable utensils, plates, and cups.
Recycle
Recycle plastic when possible to reduce waste.
Plastic is a convenient and affordable material that has become an integral part of our lives. However, the overuse of plastic has led to severe environmental and health problems. Plastic pollution harms marine life, and plastic waste takes up valuable space in landfills. Plastic also contains harmful chemicals that can leach into our food and water, posing health risks. It is essential to reduce our plastic consumption and switch to more sustainable alternatives to protect our environment and health.
About the Creator
Arun Ramasamy
Nature Lover, Just go with the flow, techno freek.
Do what you can.. don't when you cannot.





Comments
There are no comments for this story
Be the first to respond and start the conversation.