Tuberculosis (TB) is a contagious infectious disease caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It primarily affects the lungs but can also affect other parts of the body, such as the kidneys, spine, and brain. TB spreads through the air when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or speaks, releasing tiny droplets containing the bacteria.
Symptoms:
The symptoms of tuberculosis (TB) can vary depending on the stage of the disease. It's important to note that not everyone infected with the TB bacteria will develop active TB or experience symptoms. However, when symptoms do occur, they commonly include:
Persistent Cough: A cough that lasts for three weeks or longer is one of the most common symptoms of TB. Initially, the cough may be dry, but it can progress to coughing up phlegm or blood.
Chest Pain: Chest pain may occur, particularly when coughing or breathing deeply. It can be localized or spread throughout the chest.
Fatigue: Generalized tiredness, weakness, and a lack of energy are common symptoms of TB.
Weight Loss: Unintentional weight loss is a frequent symptom of active TB. It may be accompanied by a decrease in appetite.
Fever: A low-grade fever, typically in the afternoon or evening, is often present. The temperature may rise slightly above normal, but it is usually not very high.
Night Sweats: Profuse sweating during sleep, resulting in damp sheets and clothing, is a common symptom of TB.
Chills: Some individuals with active TB may experience recurring episodes of chills or shivering.
Loss of Appetite: A decreased desire to eat can lead to weight loss and further fatigue.
Shortness of Breath: If TB affects the lungs significantly, it may lead to difficulty breathing or shortness of breath.
Latent TB:
Latent tuberculosis occurs when a person is infected with the TB bacteria but does not have active symptoms. In this case, the bacteria are in a dormant state and are not causing illness. However, latent TB can progress to active TB if the immune system becomes weakened, such as in cases of HIV infection or other immunosuppressive conditions.
DIAGNOSIS:
The diagnosis of tuberculosis (TB) involves several steps to confirm the presence of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria. Healthcare professionals use various tests and examinations to diagnose TB. Here are the common methods used for TB diagnosis:
Medical History and Physical Examination: A healthcare professional will review your medical history, including any symptoms you are experiencing, and perform a physical examination. This helps to assess the likelihood of TB infection and determine which diagnostic tests to conduct.
Tuberculin Skin Test (Mantoux Test): The Mantoux test involves injecting a small amount of purified protein derivative (PPD) tuberculin into the skin, usually on the forearm. After 48 to 72 hours, a healthcare professional will check the site for a reaction. A raised, red bump at the injection site indicates a positive reaction, suggesting exposure to TB bacteria. However, this test only confirms exposure and does not distinguish between latent and active TB.
Interferon-Gamma Release Assays (IGRAs): IGRAs are blood tests that measure the release of interferon-gamma by the immune system in response to TB proteins. These tests can help differentiate between latent and active TB infections. Examples of IGRAs include the QuantiFERON-TB Gold test and the T-SPOT.TB test.
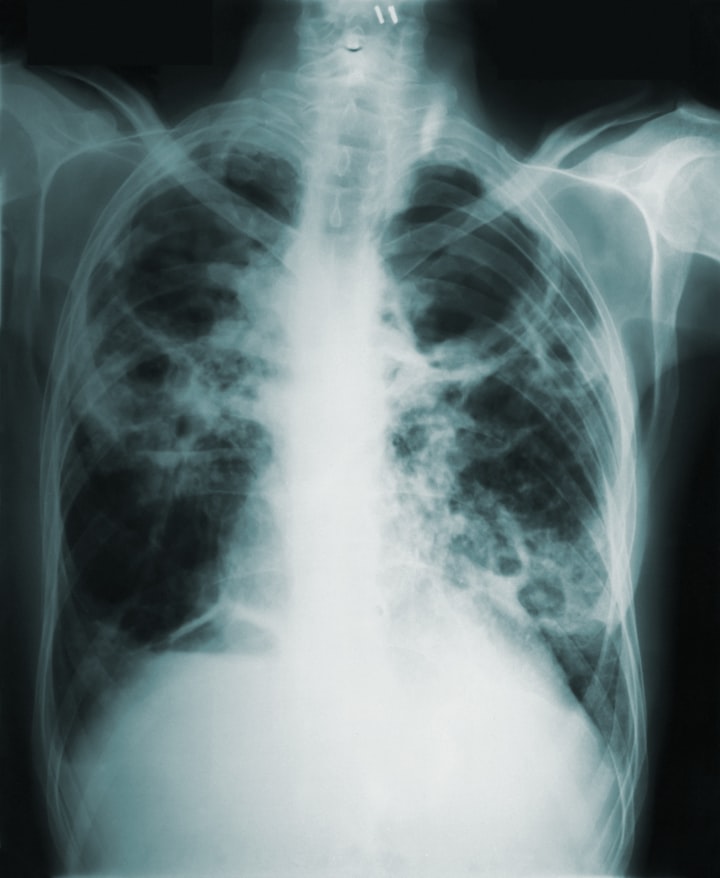
Chest X-ray: A chest X-ray is used to examine the lungs for signs of TB infection, such as the presence of abnormalities, cavities, or infiltrates. While a chest X-ray can raise suspicion of TB, it cannot provide a definitive diagnosis on its own.
Sputum Analysis: Sputum analysis involves collecting a sample of mucus from the lungs, typically by coughing it up. The sample is examined under a microscope to check for the presence of TB bacteria. In some cases, multiple samples may be required, usually collected on different days, to increase the chances of detecting the bacteria.
Molecular Tests: Molecular tests, such as nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs) or polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests, can detect the genetic material of the TB bacteria. These tests are highly sensitive and can provide rapid results. They are particularly useful for diagnosing drug-resistant TB.
Other Tests: In certain situations, additional tests may be necessary, such as cultures to isolate and identify the TB bacteria from a sputum sample or other body fluids. These tests can help determine the susceptibility of the bacteria to different antibiotics.
Treatment:
The treatment of tuberculosis (TB) involves a combination of antibiotics that need to be taken for a specified duration. The primary goal of TB treatment is to cure the infection, prevent the development of drug-resistant strains, and reduce the risk of transmission. Here are some key points regarding TB treatment:
Drug Regimen: TB treatment typically involves a combination of several antibiotics to ensure effectiveness and reduce the risk of drug resistance. The specific antibiotics used and the duration of treatment depend on factors such as the patient's age, the site of infection, drug susceptibility testing results, and whether the TB is drug-sensitive or drug-resistant.
First-line Drugs: The most commonly used antibiotics for treating TB are isoniazid, rifampin, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol. This combination is known as the first-line regimen. It is essential to take all medications as prescribed and for the entire duration of the treatment, which usually lasts for six to nine months or longer.
Directly Observed Therapy (DOT): To ensure treatment adherence and completion, healthcare providers may use a strategy called directly observed therapy. This involves healthcare workers or trained individuals directly observing the patient taking their medications to prevent missed doses.
Drug-Resistant TB: If TB is resistant to one or more of the first-line drugs, a different regimen called second-line therapy is required. Treating drug-resistant TB is more challenging and may involve a more extended treatment duration, higher numbers of medications, and potential side effects. Drug-resistant TB treatment is often guided by drug susceptibility testing to determine which antibiotics are effective against the specific strain of TB.
Side Effects: TB medications can have side effects, and it's important to discuss them with your healthcare provider. Common side effects may include nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, fatigue, and liver toxicity. Regular monitoring of potential side effects is usually done during treatment.
Follow-Up and Monitoring: Regular follow-up visits with a healthcare provider are crucial during TB treatment. This helps monitor the effectiveness of the medications, assess any side effects, and ensure treatment completion.
Infection Control: During treatment, it is important to practice good infection control measures to prevent the transmission of TB to others. This includes covering the mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing, maintaining good respiratory hygiene, and avoiding close contact with others, especially in enclosed spaces.
Prevention: TB can be prevented through various measures, including vaccination, known as the Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccine, which is recommended in countries with a high prevalence of TB. Other preventive measures include identifying and treating latent TB infections, improving ventilation in living and working spaces, practicing good respiratory hygiene, and avoiding close contact with individuals with active TB.P





Comments (1)
I'm so grateful to have found https://www.cp-investigation.com when I was scammed by this fraudulent broker. They provided me with the support and resources I needed to recover my lost funds, and they did it quickly and efficiently. The customer service was top-notch, and they gave me the assurance that my money was in safe hands. If you ever find yourself in a similar situation, I highly recommend reaching out to cp-investigation as they are trustworthy and reliable partners.