How vitamins effect our skin and body?
vitamins and their benefits

VITAMINS
• In 1912, a Polish biochemist called Casimir Funk suggested that disease might be caused by a lack of something in the diet and cured by adding it. • He thought this substance was necessary for life (vita) and contained nitrogen (amine) thus "vitamin."
• Later research showed that few of these substances contained nitrogen so the final "e" was dropped giving us the word vitamin.
• Vitamins are nutrients required in very small amounts for essential metabolic reactions in the body
• These do not include other essential nutrients i.e. dietary minerals, essential fatty acids, or essential amino acids
• Nor does the term refer to the large number of other nutrients that promote health, but are not strictly essential
• Vitamins are bio molecules that act both as catalysts & substrates in chemical reactions
• Vitamins also act as co enzymes (attach to enzymes & help in their functioning) e.g. folic acid
• Each organism has different vitamin requirements. For example, vitamin C is necessary for humans but not for dogs, because dogs can produce (synthesize) enough for their own needs, while humans cannot.
FUNCTIONS
• Vitamins are essential for the normal growth & development of a multicellular organism
• The developing fetus requires certain vitamins & minerals to be present at certain times
• These nutrients facilitate the chemical reactions that produce, among other things, skin, bone & muscle
• If there is serious deficiency in one or more of these nutrients, a child may develop a deficiency disease.

CLASSIFICATION
• There are two types of vitamins:
1.Fat soluble vitamins
2. Water soluble vitamins
FAT SOLUBLE VITAMINS
• These are absorbed, together with fat from the intestine, into the circulation
• Any disease or disorder that affects the absorption of fat, such as coeliac disease (a disease in which the small intestine is hypersensitive to gluten, leading to difficulty in digesting food), could lead to a deficiency of these vitamins
• Once absorbed into the circulation these vitamins are carried to the liver where they are stored
• When foods containing fat-soluble vitamins are eaten, the vitamins are stored in the fat tissues in body, in the liver
• Fat-soluble vitamins are easier for the body to store than water-soluble
• They go & wait around in body fat until the body needs them
• Vitamins A, D, E & K make up the fat soluble vitamins
• Vitamins A, D & K are stored in the liver & vitamin E is distributed throughout the body's fatty tissues
WATER SOLUBLE VITAMINS
• These include vitamin C & the B vitamins
• These are stored in the body for only a brief period of time
• The one exception to this is vitamin B12, which is stored in the liver
• Water-soluble vitamins need to be taken daily as they don't get stored as much in the body
• Instead, they travel through bloodstream & whatever body doesn't use, comes out when we urinate
FAT SOLUBLE VITAMINS
VITAMIN A

• Vitamin A consists of three biologically active molecules, retinol (ketone), retinal (aldehyde) and retinoic acid
• Each of these compounds is derived from the plant precursor molecule, β-carotene (a member of a family of molecules known as carotenoids)
• β–carotene consists of two molecules of retinal linked at their aldehyde ends & is referred to as pro vitamin form of vitamin A
• Helps to maintain eyes, skin, tissues and mucous membranes
• Prevents the infections brought about by low estrogen levels
• Supports vision, bone and tooth growth, immunity and reproduction Sources
• Liver, cod liver oil or other fish liver oils; egg yolks; spinach and other dark green leafy vegetables
Deficiency
• Vitamin A is stored in the liver and deficiency of the vitamin occurs only after prolonged lack of dietary intake
• The earliest symptoms of vitamin A deficiency are night blindness, increased susceptibility to infection and cancer, and anemia equivalent to iron deficient anemia
• Prolonged lack of vitamin A leads to deterioration of the eye tissue through progressive keratinization of the cornea, a condition known as xerophthalmia
• The increased risk of cancer in vitamin deficiency is thought to be due to depletion in β-carotene
• β-carotene is suspected to reduce the risk lung cancer in smokers & cancers known to be initiated by the production of free radicals
• Take care when increasing the intake of any of the lipid soluble vitamins as excess accumulation of vitamin A in the liver can lead to toxicity which manifests as bone pain, nausea and diarrhea.
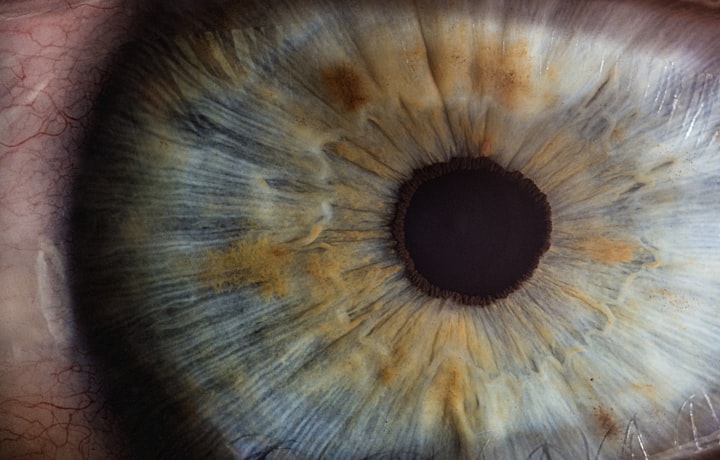
Xerophthalmia
Xerophthalmia is the abnormal dryness of the conjunctiva and cornea of the eye, with inflammation and ridge formation, typically associated with vitamin A deficiency.
VITAMIN D
• The biologically active form of this vitamin is 1,25dihydroxy vitamin D3 (calcitriol) called as cholecalciferol
• Calcitriol functions primarily to regulate calcium and phosphorous homeostasis
• Active calcitriol is derived from ergosterol (produced in plants) and from 7-dehydrocholesterol (produced in the skin)
• Ergocalciferol (vitamin D2) is formed by UV irradiation of ergosterol

FUNCTIONS
• Keep gums and muscles in good shape & help body to resist infection
• It inhibits proliferation and stimulates the differentiation of cells
• It may enhance innate immunity and inhibit the development of autoimmunity (A condition in which the body's immune system reacts against its own tissues)
• Insufficient vitamin D levels may have an adverse effect on insulin secretion
• Adequate vitamin D levels may decrease the risk of high blood pressure Innate immune system
• The innate immune system, also known as the non-specific immune system or in-born immunity system, is an important subsystem of the overall immune system that comprises the cells and mechanisms that defend the host from infection by other organisms. The cells of the innate system recognize and respond to pathogens in a generic way, but, unlike the adaptive immune system, the system does not provide long-lasting immunity to the host. Innate immune systems provide immediate defense against infection, and are found in all classes of plant and animal life. The innate immune system is an evolutionary older defense strategy, and is the dominant immune system found in plants, fungi, insects, and primitive multicellular organisms.
• The major functions of the vertebrate innate immune system include:
• Recruiting immune cells to sites of infection, through the production of chemical factors, including specialized chemical mediators, called cytokines
• Activation of the complement cascade to identify bacteria, activate cells, and promote clearance of antibody complexes or dead cells
• Identification and removal of foreign substances present in organs, tissues, blood and lymph, by specialized white blood cells
• Activation of the adaptive immune system through a process known as antigen presentation
• Acting as a physical and chemical barrier to infectious agents.
SOURCES
Sunlight, milk and other dairy products fortified with vitamin D, fish, egg yolks
DEFICIENCY
In vitamin D deficiency, calcium absorption cannot be increased enough to satisfy the body’s calcium needs
• Severe vitamin D deficiency has serious consequences for bone health and increase the risk of osteoporosis (a medical condition in which the bones become brittle and fragile from loss of tissue, typically as a result of hormonal changes) and other health problems .

• In infants and children, severe vitamin D deficiency results in the failure of bone to mineralize (rickets)
• Weight-bearing limbs (arms and legs) become bowed & in infants may result in delayed closure of the fontanels (soft spots) in the skull
• In adults bone mineral is progressively lost, resulting in bone pain and osteomalacia
• Deficiency causes muscle weakness and pain in children and adults
VITAMIN E
• The term vitamin E describes a family of eight antioxidants, four tocopherols, alpha-, beta-, gamma- and delta-, and four tocotrienols (also alpha-, beta-, gamma- and delta-)
• α-tocopherol is the only form of vitamin E that is actively maintained in the human body and is therefore, the form of vitamin E found in the largest quantities in the blood and tissue
Function
• The main function of α-tocopherol in humans appears to be that of an antioxidant
• Aside from maintaining the integrity of cell membranes throughout the body, α-tocopherol also protects the fats in low density lipoproteins (LDLs) from oxidation
• α-tocopherol is known to inhibit the activity of protein kinase C, an important cell signaling molecule, as well as to affect the expression and activity of immune and inflammatory cells
• Inhibit platelet aggregation and to enhance vasodilation
• Protects tissues against damage
• Promotes normal growth and development
• Helps in normal red blood cell formation

SOURCES
• Pure vegetable oils; wheat germ, whole meal bread and cereals, egg yoke, nuts sunflower seeds
DEFICIENCY
• Severe deficiency results mainly in neurological symptoms, including impaired balance and coordination (ataxia), injury to the sensory nerves (peripheral neuropathy), muscle weakness (myopathy), and damage to the retina of the eye (pigmented retinopathy)
• The developing nervous system appears to be especially vulnerable to vitamin E deficiency because children with severe vitamin E deficiency from birth, who are not treated with vitamin E, develop neurological symptoms rapidly
VITAMIN K
• Two naturally occurring forms of vitamin K
• Plants synthesize phylloquinone or vitamin K1
• Bacteria synthesize a range of vitamin K forms, using repeating 5-carbon units in the side chain of the molecule
• These forms of vitamin K are designated menaquinonen (MK-n), where n stands for the number of 5-carbon units
• MK-n are collectively referred to as vitamin K2
• MK-4 is produced in significant amounts by animals (including humans) from phylloquinone
• MK-4 is found in a number of organs other than the liver at higher concentrations than phylloquinone

Functions
• The major function of the K vitamins is in the maintenance of normal levels of the blood clotting proteins
• Three vitamin-K dependent proteins have been isolated in bone that reflects the importance of this vitamin in the bone mineralization
• Vitamin K-dependent protein has been found throughout the nervous system, as well in the heart, lungs, stomach, kidneys, and cartilage
Bone mineralization
Bone mineralization is the process of laying down minerals on matrix of the bone. Normal bone is composed of 50 to 70% mineral, 20 to 40% organic matrix, 5 to 10% water, and <3% lipids. Calcium and phosphorus are chief minerals found in the bone along with small amount of carbonate, magnesium
SOURCES
• Leafy green vegetables, liver, milk and yogurt
DEFICIENCY
• Naturally occurring vitamin K is absorbed from the intestines only in the presence of bile salts and other lipids through interaction with chylomicrons (transport dietary lipids from the intestines to other locations in the body)
• Therefore, fat malabsorption diseases can result in vitamin K deficiency
• Since the vitamin K2 form is synthesized by intestinal bacteria, deficiency of the vitamin in adults is rare
Chylomicrons
Chylomicrons (from the Greek chylo, meaning juice or milky fluid, and micron, meaning small particle) are lipoprotein particles that consist of triglycerides (85–92%), phospholipids (6–12%), cholesterol (1–3%), and proteins (1–2%). They transport dietary lipids from the intestines to other locations in the body.






Comments
There are no comments for this story
Be the first to respond and start the conversation.