Fetal Surgery for Spina Bifida: Advancing Treatment for Unborn Babies.
A Revolutionary Approach to Addressing a Birth Defect
Fetal Surgery for Spina Bifida:
Introduction:
Spina bifida, a congenital birth defect affecting the spine and spinal cord, poses challenges for unborn babies. However, recent medical advancements have given rise to a remarkable solution: fetal surgery. In this article, we will explore the causes of spina bifida, the diagnosis process, and the potential benefits of fetal surgery in addressing this condition.
Causes of Spina Bifida:
Spina bifida occurs when the spine and spinal cord do not develop properly during fetal development. While the exact cause is not fully understood, it is believed to be a result of a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Genetic mutations or variations can impact the development of the neural tube, which forms the spinal cord and spine. Additionally, environmental factors such as folic acid deficiency, certain medications, maternal obesity, uncontrolled diabetes, and exposure to toxins may increase the risk of spina bifida.
The primary cause of fetal surgery for spina bifida is the presence of spina bifida itself. Spina bifida is a congenital birth defect that occurs during the early stages of fetal development when the spine and spinal cord do not form properly. The exact cause of spina bifida is not fully understood, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Genetic factors: Certain genetic mutations or variations can increase the risk of spina bifida. These mutations can affect the development of the neural tube, which eventually forms the baby's spinal cord and spine. Genetic factors can play a role in determining the severity of the condition as well.
Environmental factors: Several environmental factors during pregnancy have been associated with an increased risk of spina bifida. These factors include a deficiency of folic acid (a B vitamin), certain medications, maternal obesity, uncontrolled diabetes, and exposure to certain chemicals or toxins.
It's important to note that not all cases of spina bifida require fetal surgery. The decision to perform fetal surgery is typically based on the severity of the condition and the potential benefits outweighing the risks. Fetal surgery aims to address the spinal defect and reduce the risk of further damage to the baby's spinal cord and nerves, potentially improving their long-term outcomes.
It is crucial for expectant parents to work closely with their healthcare providers to understand the specific causes and factors contributing to spina bifida in their case. This allows for informed decision-making regarding fetal surgery and other appropriate interventions.
Diagnosing Spina Bifida:
During the 18th to 20th week of pregnancy, an anomaly scan is conducted to assess the baby's anatomy. This comprehensive screening test includes an examination of the spine. If spina bifida is detected, it signifies that the spinal bones have not fully closed, potentially leading to damage to the spinal cord and nerves.
Fetal Surgery: A Promising Solution:
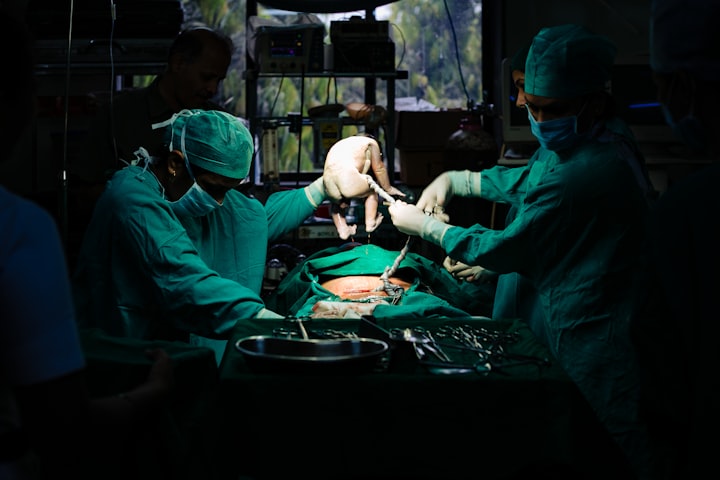
Fetal surgery provides a means to address spina bifida and minimize future complications. One notable technique is open fetal surgery, wherein a skilled surgical team partially or completely removes the baby from the uterus to repair the spinal defect. This intricate procedure is typically performed in specialized medical centers equipped with the necessary expertise.
The Procedure and Post-Surgery Care:
After repairing the spinal defect, the baby is carefully placed back into the uterus, and the mother's abdomen is closed. Fetal surgery aims to mitigate the risk of further damage to the baby's spinal cord and improve long-term outcomes. Following the surgery, it is common for mothers to feel their unborn baby wriggling or moving in the womb, a positive sign indicating the baby's activity and responsiveness.
Considerations and Potential Benefits:
While fetal surgery for spina bifida offers promising benefits, it is vital to acknowledge the associated risks and potential complications. The decision to undergo this procedure is made on a case-by-case basis, considering factors such as the severity of the condition, gestational age, and maternal health. Consulting with a qualified healthcare professional is crucial for obtaining accurate and personalized information.
Conclusion:
Fetal surgery for spina bifida represents a groundbreaking approach in prenatal medicine. This procedure provides hope to families grappling with the challenges of spina bifida by addressing the spinal defect before birth. While the decision to pursue fetal surgery requires careful consideration, its potential benefits in reducing complications and improving long-term outcomes make it a viable option. If you or a loved one is affected by spina bifida, seeking guidance from a qualified healthcare professional is paramount for informed decision-making and personalized care.
Note: The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice.




Comments
There are no comments for this story
Be the first to respond and start the conversation.