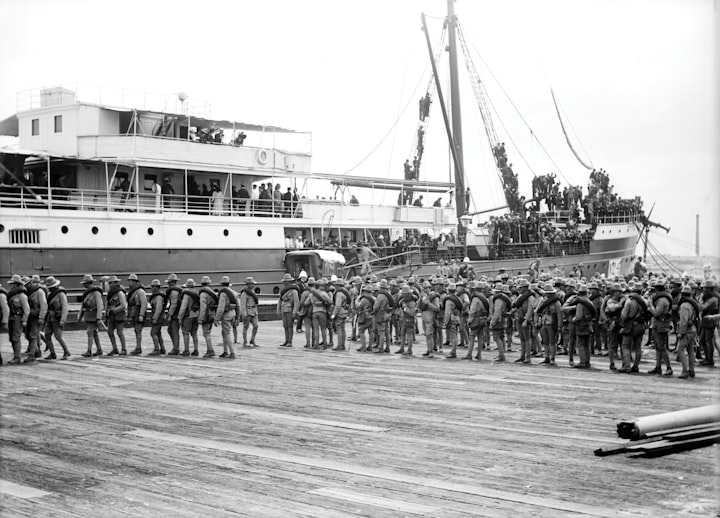

From 1946 to 1991 the United States, the Soviet Union, and its allies were imprisoned in a long and bitter war known as the Cold War. The Cold War was rooted in a war of attrition and the political stance of global influence between the Soviet Union and the United States after their temporary alliance following the 1945 German occupation. Historians disagree on a certain date, but it is widely believed that the war lasted from 1947, with Truman Doctrine, to 1991, with the dissolution of the USSR.
The Cold War was an ongoing political conflict between the United States, the Soviet Union, and its allies after the second world war. Although both countries were peaceful, the long, intense debate known as the Cold War was marked by fierce arms races, legal battles, and the quest for world domination. The term Cold War has existed since the 1930s when it was first used to describe strained relations between European nations.
After World War II, the United States and its allies, the Soviet Union, and its satellite nation launched a decades-long struggle for independence known as the Cold War. The Soviet Union and the United States fought each other against other nations through political means, military alliances, intelligence, propaganda, weapons, economic aid, and representative wars. Soldiers from both nations were not at war during the Cold War.
The Cold War, fought by the Soviet Union for 40 years between the end of World War II and the fall of the Berlin Wall, divided the country into separate maps, with many nations under Communist rule and some intervening in American military intervention.
The Soviet Union sent troops to maintain communism in East Germany (1953), Hungary (1956), Czechoslovakia (1968), and Afghanistan (1979) to strengthen communism. The United States overthrew Guatemala's left-wing government (1954), backed the unsuccessful invasion of Cuba (1961), invaded the Dominican Republic (1965) and Grenada (1982) launched a failed war, which lasted for decades in Vietnam, dividing America's population. Assuming the West was victorious, the victory could have been opposed by communist China.
The struggle to overthrow the colonial powers was embroiled in the Cold War conflicts as the superpowers influenced the anti-colonial movement. The West, led by the United States and other First World nations of the Western Bloc, had free democratic communications in its former colonies with a network of dictatorial nations.
In 1949, the Communists won a decisive victory over the Chinese civil war, and the world's most populous nation joined the Soviet Union as an enemy of the Cold War. North Korea invaded South Korea in 1950 and sent troops and military aid to the United Nations and the United States. The 1962 Cuban Missile Crisis brought countries closer to real wars than any other Cold War event.
In the early 1960s, President Kennedy faced a series of personal concerns. Fighting insurgency at home has shown growing concern about the Soviet threat abroad.
The Americans suspected Soviet communism and were concerned about the dictatorship of Russian dictator Joseph Stalin in his country. The first military action of the Cold War began in June 1950 when the Soviet-backed Soviet People's Army attacked its western neighbor. Many American officials fear that this is the first step in a communist campaign to overthrow the country and view it as unimportant as an alternative.
The Soviets, for their part, were outraged by the decades-long American refusal to rule the USSR as an official part of international society, and their delay in entering World War II, which resulted in the death of tens of millions of Russians.
Although the United States has not committed itself to change the long-standing tradition of distance from European affairs, Roosevelt assured Stalin in Tehran that US troops would return home within two years of the end of the war. With the suppression of the oppressive 1930s and the assurance that economic growth would continue during the war, democracy was concentrated only in a few countries where it already existed. As a result, the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, which ended World War II, were the dictatorial world power. The obvious fact that the Americans and the British would not have defeated Hitler without Stalin's help meant that the war was a victory for apartheid, not dictatorship and its hope for the future.
Truman's administration followed a comprehensive content strategy, which, to put it bluntly, was a major effort to build a wall around the communist world that would be protected by the United States military and its allies. The sacrifices made by many members of the service made the US and its allies after the collapse of the Soviet Union a threat to the rise of communism. The US Army, its warships, planes, and sailors guarded the walls against the beginning of the Cold War to the end.
About the Creator
Radha Karki
I am very curious ar learning new things, love to read books, paintings, art, and love singing too.




Comments
There are no comments for this story
Be the first to respond and start the conversation.