Murder Hornets’ in the U.S
The Rush to Stop the Asian Giant Hornet
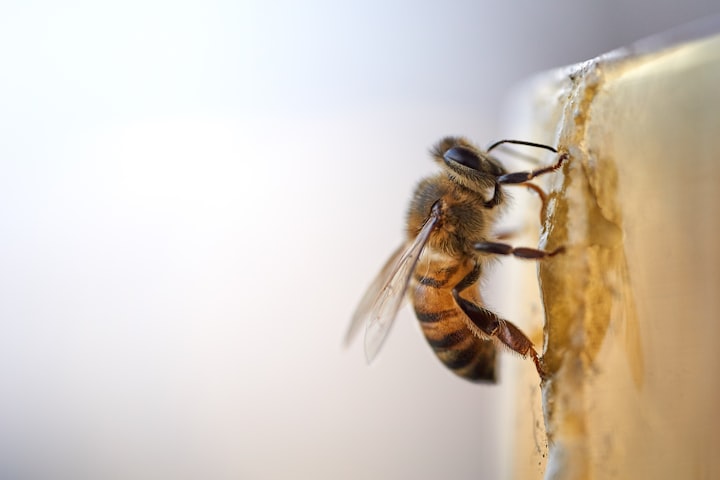

As of my last knowledge update in September 2021, there were reports of "murder hornets" in the United States. The term "murder hornets" refers to the Asian giant hornet (Vespa mandarinia), which is the world's largest hornet species. These hornets gained significant media attention in 2020 when a few of them were discovered in Washington state and subsequently eradicated.
The Asian giant hornets are native to East Asia, particularly Japan and South Korea. They are known for their large size, aggressive behavior, and potent sting, which can be harmful or even deadly to humans, especially if a person is allergic to insect stings. However, it's important to note that deaths caused by these hornets are rare.
Efforts have been made to track and eliminate any Asian giant hornets in the United States to prevent them from establishing a population and becoming an invasive species. Authorities and beekeepers are particularly concerned about their potential impact on honeybee populations, as these hornets can decimate beehives.
For the most up-to-date and accurate information on the current situation regarding murder hornets in the U.S., I recommend consulting local news sources or contacting relevant agricultural and environmental authorities in your area.
Dealing with hornets can be challenging due to their aggressive nature and potentially painful stings. Here are some general guidelines for dealing with hornets:
Avoid provoking them: Hornets are protective of their nests and can become aggressive if they feel threatened. Be cautious around their nests and avoid sudden movements or loud noises that may provoke them.
Stay calm and move away slowly: If you encounter hornets or disturb their nest, try to stay calm and slowly move away without swatting at them. Quick movements can provoke an attack.
Do not disturb their nests: Avoid tampering with or attempting to remove a hornet nest on your own. Hornets can defend their nests fiercely, and attempting removal without professional expertise can be dangerous.
Seek professional help: If you have a hornet nest on your property or near your home, it is best to contact a professional pest control service or local beekeeper. They have the knowledge, experience, and protective equipment to handle the situation safely and effectively.
Wear protective clothing: If you must be in an area where hornets are present, wear long sleeves, long pants, closed-toe shoes, and a hat. This clothing can provide some protection against hornet stings.
Use insect repellents: Some insect repellents may be effective in deterring hornets. Look for products specifically labeled for hornets or wasps and follow the instructions carefully.
Maintain cleanliness: Hornets are attracted to food and sugary substances. Keep outdoor eating areas clean and free of spills, and ensure garbage cans are tightly sealed.
Remember, dealing with hornets can be dangerous, especially if you have an allergy to their stings. It is always advisable to seek professional assistance to handle hornet nests or infestations.
The lifespan of hornets can vary depending on the species. Generally, the lifespan of a hornet can range from a few weeks to several months. Here are some approximate lifespan ranges for different types of hornets:
Asian giant hornet (Vespa mandarinia): The workers typically live for a few weeks to a month. The queens can live for several months, typically surviving through the winter to establish new colonies the following year.
European hornet (Vespa crabro): The workers typically live for a few weeks to a month, while the queens can live for several months. Similar to Asian giant hornets, European hornet queens can survive over the winter to establish new colonies.
Bald-faced hornet (Dolichovespula maculata): The lifespan of the workers is around a few weeks, while the queens can live for several months. Again, the queens have the ability to overwinter and start new colonies in the spring.
It's important to note that the lifespan of individual hornets within a colony can vary due to factors such as their role (worker or queen) and the time of year. Workers, which are sterile females, have shorter lifespans as they primarily engage in foraging and nest maintenance tasks. Queens, on the other hand, have the ability to reproduce and establish new colonies, so they have longer lifespans.
These lifespan estimates are based on general knowledge about hornets, but it's worth mentioning that specific circumstances and environmental conditions can influence their longevity.




Comments
There are no comments for this story
Be the first to respond and start the conversation.