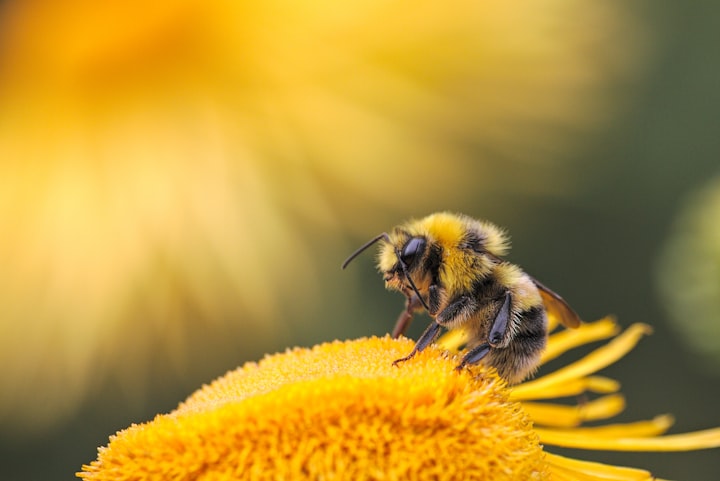

Bees are fascinating creatures that belong to the insect order Hymenoptera and the superfamily Apoidea. They are closely related to wasps and ants and play a vital role in the ecosystem as pollinators. With over 20,000 known species, bees can be found on every continent except Antarctica, inhabiting a wide range of habitats, from forests and meadows to deserts and urban areas.
The anatomy of bees is uniquely adapted to their role as efficient pollinators. Like other insects, bees have three main body regions: the head, thorax, and abdomen. Their bodies are covered in a layer of hairs that aid in the collection and transportation of pollen. Bees also possess two pairs of wings, which they use to navigate and hover near flowers.
One of the most distinctive features of bees is their specialized feeding apparatus. They have a long, tube-like structure called a proboscis that enables them to extract nectar from flowers. The proboscis acts like a straw, allowing bees to reach deep into the flower to access the sweet reward. Some bees, such as honeybees, also have specialized structures on their legs called pollen baskets or corbiculae. These concave regions are used to carry and transport pollen back to the hive.
The life cycle of a bee consists of four stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult. After mating, the queen bee lays eggs in the cells of the hive. These eggs hatch into larvae, which are fed a mixture of pollen and nectar by the worker bees. The larvae grow rapidly, molting several times before entering the pupal stage. Inside the pupa, the bee undergoes metamorphosis, with its body structures and organs developing and taking shape. Finally, an adult bee emerges from the pupal case, ready to contribute to the hive.
Bees exhibit a high level of social organization, with complex colony structures and division of labor. Most bees are eusocial, meaning they live in large colonies where individuals have specialized roles. A typical bee colony consists of a queen, worker bees, and drones. The queen's primary role is to reproduce and lay eggs, ensuring the survival of the colony. Worker bees, which are all female, perform various tasks, including foraging for food, building and maintaining the hive, and caring for the young. Drones, on the other hand, are male bees whose sole purpose is to mate with the queen.
Communication among bees is essential for colony coordination. Bees communicate using a combination of visual cues, pheromones, and intricate dance-like movements known as the "waggle dance." The waggle dance conveys information about the location of food sources, allowing worker bees to efficiently collect nectar and pollen.
As pollinators, bees play a critical role in plant reproduction and the maintenance of biodiversity. When bees visit flowers to collect nectar, they inadvertently transfer pollen from the male parts of one flower to the female parts of another. This cross-pollination enables plants to produce fruits and seeds, ensuring their survival and genetic diversity. Bees are estimated to be responsible for pollinating a significant portion of the world's flowering plant species, including many crops that are vital for human food production.
However, bees face numerous challenges today, including habitat loss, pesticide exposure, and climate change. These factors have led to a decline in bee populations worldwide, posing a threat to ecosystems and agricultural productivity. Efforts are underway to protect bees and their habitats through the creation of pollinator-friendly environments, reduction of pesticide use, and public awareness campaigns.
In conclusion, bees are remarkable insects with unique adaptations and complex social structures. Their crucial role as pollinators makes them essential for maintaining





Comments
There are no comments for this story
Be the first to respond and start the conversation.